HashSet in java
HashSet implements Set interface.It is a collection that contains no duplicate elements. HashSet is unordered.
Let us undertsand Internal working of HashSet using the below example. The example contains Employee class with two members id and name. We are implementing the hashcode , equals and toString methods.
Demo 1:
[Employee [id=2, name=Robert], Employee [id=1, name=Jack], Employee [id=2, name=Nancy], Employee [id=2, name=Tom]]
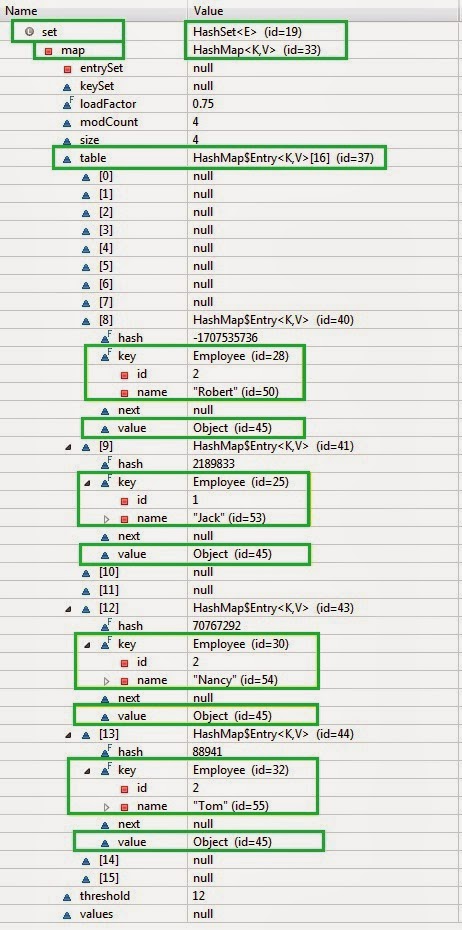
HashSet uses HashMap internally. The value added to set is added as a key to HashMap and the value is a dummy static object. the above output shows that the data is unordered. The add method of HashSet call the put method of HashMap internally.
Conclusion: HashSet uses HashMap internally and so it is best practice to implement hashcode and equals for the class , whose object is added in HashSet.The element of set is stored as key and the static object(dummy Object) of Object class is stored as value of HashMap.
HashSet implements Set interface.It is a collection that contains no duplicate elements. HashSet is unordered.
Let us undertsand Internal working of HashSet using the below example. The example contains Employee class with two members id and name. We are implementing the hashcode , equals and toString methods.
Demo 1:
import java.util.HashSet;
/**
*
* @author Ganesh.Rashinker
*
*/
class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
public Employee(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
/**
*
* @author Ganesh.Rashinker
*
*/
class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
public Employee(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Employee> set = new HashSet<Employee>();
Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Jack");
Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Robert");
Employee emp3 = new Employee(2, "Nancy");
Employee emp4 = new Employee(2, "Tom");
set.add(emp1);
set.add(emp2);
set.add(emp3);
set.add(emp4);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
Output:public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<Employee> set = new HashSet<Employee>();
Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Jack");
Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Robert");
Employee emp3 = new Employee(2, "Nancy");
Employee emp4 = new Employee(2, "Tom");
set.add(emp1);
set.add(emp2);
set.add(emp3);
set.add(emp4);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
[Employee [id=2, name=Robert], Employee [id=1, name=Jack], Employee [id=2, name=Nancy], Employee [id=2, name=Tom]]
HashSet uses HashMap internally. The value added to set is added as a key to HashMap and the value is a dummy static object. the above output shows that the data is unordered. The add method of HashSet call the put method of HashMap internally.
Conclusion: HashSet uses HashMap internally and so it is best practice to implement hashcode and equals for the class , whose object is added in HashSet.The element of set is stored as key and the static object(dummy Object) of Object class is stored as value of HashMap.

Great explanation !
ReplyDeletenice
ReplyDeleteExcellent..
ReplyDelete